- +91-8745023101
- Join Online :Click for view course contents

There are three types of errors:
Escape characters (Backslash) is used when working with special characters like single quotes, double quotes, apostrophes and ampersands. Place backslash before the characters to make it display.
Example:
document.write "I m a "good" boy"
document.write "I m a "good" boy"
An alert box displays only one button which is the OK button.
But a Confirmation box displays two buttons namely OK and cancel.
"==" checks only for equality in value whereas "===" is a stricter equality test and returns false if either the value or the type of the two variables are different.
To submit a form using JavaScript use document.form[0].submit();
document.form[0].submit();
Timers are used to execute a piece of code at a set time or also to repeat the code in a given interval of time. This is done by using the functions setTimeout, setInterval and clearInterval.
The setTimeout(function, delay) function is used to start a timer that calls a particular function after the mentioned delay. The setInterval(function, delay) function is used to repeatedly execute the given function in the mentioned delay and only halts when cancelled. The clearInterval(id) function instructs the timer to stop.
Timers are operated within a single thread, and thus events might queue up, waiting to be executed.
// for Single line comments and
/* Multi
Line
Comment
*/
I am assuming that js file name is message.js, place the following script tag inside the head tag.
<script type="text/javascript" src="message.js"></script>
A simple example of JavaScript hello world is given below. You need to place it inside the body tag of HTML.
<script type="text/javascript">
document.write("JavaScript Hello World!");
</script>
Netscape provided the JavaScript language. Microsoft changed the name and called it JScript to avoid the trademark issue. In other words, you can say JScript is the same as JavaScript, but Microsoft provides it.
The function which has named at the time of definition is called a named function. For example
function msg()
{
document.write("Named Function");
}
msg();
Some of the disadvantages of JavaScript are:
Some of the advantages of JavaScript are:
Some of the features of JavaScript are:
JavaScript is a scripting language. It is different from Java language. It is object-based, lightweight, cross-platform translated language. It is widely used for client-side validation. The JavaScript Translator (embedded in the browser) is responsible for translating the JavaScript code for the web browser.
DISTINCT is converted to a GROUP BY on all columns and it will be combined with ORDER BY clause.
|
|
SELECT DISTINCT t1.a FROM t1,t2 where t1.a=t2.a;
|
The = , <>, <=, <, >=, >,<<,>>, <=>, AND, OR, or LIKE operators are used in column comparisons in SELECT statements.
CHAR_LENGTH is character count whereas the LENGTH is byte count. The numbers are same for Latin characters but they are different for Unicode and other encodings.
Majorly SQL commands can be divided into three categories, i.e., DDL, DML & DCL. Data Definition Language (DDL) deals with all the database schemas, and it defines how the data should reside in the database. Commands like CreateTABLE and ALTER TABLE are part of DDL.
Data Manipulative Language (DML) deals with operations and manipulations on the data. The commands in DML are Insert, Select, etc.
Data Control Languages (DCL) are related to the Grant and permissions. In short, the authorization to access any part of the database is defined by these.
Following are the drivers available in MySQL:
To identify each row of a table, we will use a primary key. For a table, there exists only one primary key.
A candidate key is a column or a set of columns, which can be used to uniquely identify any record in the database without having to reference any other data.
Federated tables are tables that point to the tables located on other databases on some other server.
In MySQL, the "i-am-a-dummy" flag makes the MySQL engine to deny the UPDATE and DELETE commands unless the WHERE clause is present.
In MySQL, regular expressions are used in queries for searching a pattern in a string.
Example:
The following statement retrieves all rows where column employee_name contains the text 1000 (example salary):
Select employee_name
From employee
Where employee_name REGEXP '1000'
Order by employee_name
MySQL data directory is a place where MySQL stores its data. Each subdirectory under this data dictionary represents a MySQL database. By default, the information managed my MySQL = server mysqld is stored in the data directory.
Mysql_close() cannot be used to close the persistent connection. However, it can be used to close a connection opened by mysql_connect().
Mysql_fetch_object is used to retrieve the result from the database as objects, while mysql_fetch_array returns result as an array. This will allow access to the data by the field names.
For example:
Using mysql_fetch_object field can be accessed as $result->name.
Using mysql_fetch_array field can be accessed as $result->[name].
Using mysql_fetch_row($result) where $result is the result resource returned from a successful query executed using the mysql_query() function.
MyISAM follows a conservative approach to disk space management and stores each MyISAM table in a separate file, which can be further compressed if required. On the other hand, InnoDB stores the tables in the tablespace. Its further optimization is difficult.
MyISAM table is stored on disk in three formats.
SELECT team_name FROM team WHERE team_won IN (1, 3, 5, 7);
SELECT COUNT user_id FROM users;
SELECT * FROM table_name LIMIT 0,20;
NOW() command is used to show current year, month, date with hours, minutes, and seconds while CURRENT_DATE() shows the current year with month and date only.
If you want to display the current date and time, use -
SELECT NOW();
If you want to display the current date only, use:
SELECT CURRENT_DATE();
You can a create maximum of 16 indexed columns for a standard table.
REGEXP is a pattern match using a regular expression. The regular expression is a powerful way of specifying a pattern for a sophisticated search.
Basically, it is a special text string for describing a search pattern. To understand it better, you can think of a situation of daily life when you search for .txt files to list all text files in the file manager. The regex equivalent for .txt will be .*.txt.
Let us take a table named the employee.
To find Nth highest salary is:
select distinct(salary)from employee order by salary desc limit n-1,1
if you want to find 3rd largest salary:
select distinct(salary)from employee order by salary desc limit 2,1
The "i_am_a_dummy flag" enables the MySQL engine to refuse any UPDATE or DELETE statement to execute if the WHERE clause is not present. Hence it can save the programmer from deleting the entire table my mistake if he does not use WHERE clause.
Mysql_connect:
Mysql_pconnect:
FLOAT stores floating-point numbers with accuracy up to 8 places and allocate 4 bytes. On the other hand, DOUBLE stores floating-point numbers with accuracy up to 18 places and allocates 8 bytes.
Heap tables:
Heap tables are found in memory that is used for high-speed storage temporarily. They do not allow BLOB or TEXT fields.
Heap tables do not support AUTO_INCREMENT.
Indexes should be NOT NULL.
Temporary tables:
The temporary tables are used to keep the transient data. Sometimes it is beneficial in cases to hold temporary data. The temporary table is deleted after the current client session terminates.
Main differences:
The heap tables are shared among clients, while temporary tables are not shared.
Heap tables are just another storage engine, while for temporary tables, you need a special privilege (create temporary table).
BLOB is an acronym that stands for a large binary object. It is used to hold a variable amount of data.
There are four types of the BLOB.
The differences among all these are the maximum length of values they can hold.
TEXT is a case-insensitive BLOB. TEXT values are non-binary strings (character string). They have a character set, and values are stored and compared based on the collation of the character set.
There are four types of TEXT.
Tables that are present in memory is known as HEAP tables. When you create a heap table in MySQL, you should need to specify the TYPE as HEAP. These tables are commonly known as memory tables. They are used for high-speed storage on a temporary basis. They do not allow BLOB or TEXT fields.
A trigger is a set of codes that executes in response to some events.
There are only six Triggers allowed to use in the MySQL database.
Working with the MySQL server, it is a common task to view or list the available databases. We can view all the databases on the MySQL server host using the following command:
SHOW DATABASES;
Indexing is a process to find an unordered list into an ordered list. It helps in maximizing the query's efficiency while searching on tables in MySQL. The working of MySQL indexing is similar to the book index.
Suppose we have a book and want to get information about, say, searching. Without indexing, it is required to go through all pages one by one, until the specific topic was not found. On the other hand, an index contains a list of keywords to find the topic mentioned on pages. Then, we can flip to those pages directly without going through all pages.
Sometimes we need to fetch data from three or more tables. There are two types available to do these types of joins. Suppose we have three tables named Student, Marks, and Details.
Let's say Student has (stud_id, name) columns, Marks has (school_id, stud_id, scores) columns, and Details has (school_id, address, email) columns.
1. Using SQL Join Clause
This approach is similar to the way we join two tables. The following query returns result from three tables:
SELECT name, scores, address, email FROM Student s
INNER JOIN Marks m on s.stud_id = m.stud_id
INNER JOIN Details d on d.school_id = m.school_id;
2. Using Parent-Child Relationship
It is another approach to join more than two tables. In the above tables, we have to create a parent-child relationship. First, create column X as a primary key in one table and as a foreign key in another table. Therefore, stud_id is the primary key in the Student table and will be a foreign key in the Marks table. Next, school_id is the primary key in the Marks table and will be a foreign key in the Details table. The following query returns result from three tables:
SELECT name, scores, address, email
FROM Student s, Marks m, Details d
WHERE s.stud_id = m.stud_id AND m.school_id = d.school_id;
The MySQL Inner Join is used to returns only those results from the tables that match the specified condition and hides other rows and columns. MySQL assumes it as a default Join, so it is optional to use the Inner Join keyword with the query.
We can understand it with the following visual representation where Inner Joins returns only the matching results from table1 and table2:
MySQL Inner Join Syntax:
The Inner Join keyword is used with the SELECT statement and must be written after the FROM clause. The following syntax explains it more clearly:
SELECT columns
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2 ON condition1
INNER JOIN table3 ON condition2
...;
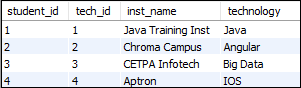
Let us first create two tables "students" and "technologies" that contains the following data:
Table: student
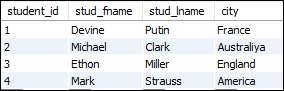
Table: technologies
To select records from both tables, execute the following query:
SELECT students.stud_fname, students.stud_lname, students.city, technologies.technology
FROM students
INNER JOIN technologies
ON students.student_id = technologies.tech_id;
After successful execution of the query, it will give the following output:
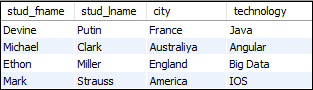
We can connect two or more tables in MySQL using the JOIN clause. MySQL allows various types of JOIN clauses. These clauses connect multiple tables and return only those records that match the same value and property in all tables. The following are the four easy ways to join two or more tables in MySQL:
We can delete a row from the MySQL table using the DELETE STATEMENT within the database. The following is the generic syntax of DELETE statement in MySQL to remove one or more rows from a table:
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE Condition_specified;
We can insert data in a MySQL table using the INSERT STATEMENT. This statement allows us to insert single or multiple rows into a table. The following is the basic syntax to insert a record into a table:
INSERT INTO table_name ( field1, field2,...fieldN )
VALUES ( value1, value2,...valueN );
If we want to insert more than one rows into a table, use the below syntax:
INSERT INTO table(field1, field2,...fieldN)
VALUES
(value1, value 2, ...),
(value1, value2, ...),
...
(value1, value2, ...);
We can remove, drop, or delete one or more columns in an existing table using the ALTER TABLE statement as follows:
ALTER TABLE table_name DROP COLUMN column_name1, column_name2....;
While creating a table, we have kept one of the column names incorrectly. To change or rename an existing column name in MySQL, we need to use the ALTER TABLE and CHANGE commands together. The following are the syntax used to rename a column in MySQL:
ALTER TABLE table_name
CHANGE COLUMN old_column_name new_column_name column_definition [FIRST|AFTER existing_column];
We can delete a table in MySQL using the Drop Table statement. This statement removes the complete data of a table, including structure and definition from the database permanently. Therefore, it is required to be careful while deleting a table. After using the statement, we cannot recover the table in MySQL. The statement is as follows:
DROP TABLE table_name;
A column is a series of cells in a table that stores one value for each row in a table. We can add columns in an existing table using the ALTER TABLE statement as follows:
ALTER TABLE table_name
ADD COLUMN column_name column_definition [FIRST|AFTER existing_column];
There are many tables that remain present by default. But, MyISAM is the default database engine used in MySQL. There are five types of tables that are present:
irst of all, the MYSQL server is free to use for developers and small enterprises.
MySQL server is open source.
MySQL's community is tremendous and supportive; hence any help regarding MySQL is resolved as soon as possible.
MySQL has very stable versions available, as MySQL has been in the market for a long time. All bugs arising in the previous builds have been continuously removed, and a very stable version is provided after every update.
The MySQL database server is very fast, reliable, and easy to use. You can easily use and modify the software. MySQL software can be downloaded free of cost from the internet.
The default port for MySQL server is 3306.
There is a major difference between a database and a table. The differences are as follows:
MySQL has the following technical specifications -
SQL is known as the standard query language. It is used to interact with the database like MySQL. MySQL is a database that stores various types of data and keeps it safe.
A PHP script is required to store and retrieve the values inside the database.
SQL is a computer language, whereas MySQL is a software or an application
SQL is used for the creation of database management systems whereas MySQL is used to enable data handling, storing, deleting and modifying data
MySQL is written in C and C++, and its SQL parser is written in yacc.
MySQL is a multithreaded, multi-user SQL database management system which has more than 11 million installations. It is the world's second most popular and widely-used open source database. It is interesting how MySQL name was given to this query language. The term My is coined by the name of the daughter of co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter, and SQL is the short form of Structured Query Language. Using MySQL is free of cost for the developer, but enterprises have to pay a license fee to Oracle.
Formerly MySQL was initially owned by a for-profit firm MySQL AB, then Sun Microsystems bought it, and then Oracle bought Sun Microsystems, so Oracle currently owns MySQL.
MySQL is an Oracle-supported Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) based on structured query language. MySQL supports a wide range of operating systems, most famous of those include Windows, Linux & UNIX. Although it is possible to develop a wide range of applications with MySQL, it is only used for web applications & online publishing. It is a fundamental part of an open-source enterprise known as Lamp.
PHP parser parses the PHP developed website from the opening to the closing tag. Tags indicate that from where PHP code is being started and ended. In other words, opening and closing tags decide the scope of PHP scripting syntax of closing tag in PHP
<?php syntax of opening tag in PHP
?> syntax of closing tag in PHP
$_SERVER − This is an array containing information such as headers, paths, and script locations. The entries in this array are created by the web server. There is no guarantee that every web server will provide any of these.
The following table lists the most important elements that can go inside $_SERVER:
| Element/Code | Description |
|---|---|
| $_SERVER['PHP_SELF'] | Returns the filename of the currently executing script |
| $_SERVER['GATEWAY_INTERFACE'] | Returns the version of the Common Gateway Interface (CGI) the server is using |
| $_SERVER['SERVER_ADDR'] | Returns the IP address of the host server |
| $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'] | Returns the name of the host server (such as www.sstechlab.com) |
| $_SERVER['SERVER_SOFTWARE'] | Returns the server identification string (such as Apache/2.2.24) |
| $_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] | Returns the name and revision of the information protocol (such as HTTP/1.1) |
| $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] | Returns the request method used to access the page (such as POST) |
| $_SERVER['REQUEST_TIME'] | Returns the timestamp of the start of the request (such as 1377687496) |
| $_SERVER['QUERY_STRING'] | Returns the query string if the page is accessed via a query string |
| $_SERVER['HTTP_ACCEPT'] | Returns the Accept header from the current request |
| $_SERVER['HTTP_ACCEPT_CHARSET'] | Returns the Accept_Charset header from the current request (such as utf-8,ISO-8859-1) |
| $_SERVER['HTTP_HOST'] | Returns the Host header from the current request |
| $_SERVER['HTTP_REFERER'] | Returns the complete URL of the current page (not reliable because not all user-agents support it) |
| $_SERVER['HTTPS'] | Is the script queried through a secure HTTP protocol |
| $_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'] | Returns the IP address from where the user is viewing the current page |
| $_SERVER['REMOTE_HOST'] | Returns the Host name from where the user is viewing the current page |
| $_SERVER['REMOTE_PORT'] | Returns the port being used on the user's machine to communicate with the web server |
| $_SERVER['SCRIPT_FILENAME'] | Returns the absolute pathname of the currently executing script |
| $_SERVER['SERVER_ADMIN'] | Returns the value given to the SERVER_ADMIN directive in the web server configuration file (if your script runs on a virtual host, it will be the value defined for that virtual host) (such as someone@sstechlab.com) |
| $_SERVER['SERVER_PORT'] | Returns the port on the server machine being used by the web server for communication (such as 80) |
| $_SERVER['SERVER_SIGNATURE'] | Returns the server version and virtual host name which are added to server-generated pages |
| $_SERVER['PATH_TRANSLATED'] | Returns the file system based path to the current script |
| $_SERVER['SCRIPT_NAME'] | Returns the path of the current script |
| $_SERVER['SCRIPT_URI'] | Returns the URI of the current page |
This is a global PHP variable. This variable is an associate double dimension array and keeps all the information related to uploaded file.
Here is the example to unset a single variable −
<?php
unset($_SESSION['counter']);
?>
Singly quoted strings are treated almost literally, whereas doubly quoted strings replace variables with their values as well as specially interpreting certain character sequences.
<?php $variable = "name"; $literally = 'My $variable will not print!\n'; print($literally); print "<br />"; $literally = "My $variable will print!\n"; print($literally); ?>
This will produce following result −
My $variable will not print! My name will print
The PHP $_REQUEST variable contains the contents of both $_GET, $_POST, and $_COOKIE. We will discuss $_COOKIE variable when we will explain about cookies. The PHP $_REQUEST variable can be used to get the result from form data sent with both the GET and POST methods.
There is no need to write a dollar sign ($) before a constant, where as in Variable one has to write a dollar sign.
Constants cannot be defined by simple assignment, they may only be defined using the define() function.
Constants may be defined and accessed anywhere without regard to variable scoping rules.
Once the Constants have been set, may not be redefined or undefined.
To define a constant you have to use define() function and to retrieve the value of a constant, you have to simply specifying its name. Unlike with variables, you do not need to have a constant with a $.
As indicated by the name, this function will return the value of the constant. This is useful when you want to retrieve value of a constant, but you do not know its name, i.e. It is stored in a variable or returned by a function.
<?php
define("MINSIZE", 50);
echo MINSIZE;
echo constant("MINSIZE"); // same thing as the previous line
?>
Only scalar data (boolean, integer, float and string) can be contained in constants.
NULL is a special type that only has one value: NULL. To give a variable the NULL value, simply assign it like this −
$my_var = NULL;
The special constant NULL is capitalized by convention, but actually it is case insensitive; you could just as well have typed −
$my_var = null;
A variable that has been assigned NULL has the following properties:
It evaluates to FALSE in a Boolean context.
It returns FALSE when tested with IsSet() function.
PHP has a total of eight data types which we use to construct our variables −
Integers − are whole numbers, without a decimal point, like 4195.
Doubles − are floating-point numbers, like 3.14159 or 49.1.
Booleans − have only two possible values either true or false.
NULL − is a special type that only has one value: NULL.
Strings − are sequences of characters, like 'PHP supports string operations.'
Arrays − are named and indexed collections of other values.
Objects − are instances of programmer-defined classes, which can package up both other kinds of values and functions that are specific to the class.
Resources − are special variables that hold references to resources external to PHP (such as database connections).
If the function require() cannot access the file then it ends with a fatal error. However, the include() function gives a warning, and the PHP script continues to execute.
Answer: No. PHP is a weakly typed or loosely typed language.
This means PHP does not require to declare data types of the variable when you declare any variable like the other standard programming languages C# or Java. When you store any string value in a variable, then the data type is the string and if you store a numeric value in that same variable then the data type is an Integer.
Sample code:
$var = "Hello"; //String$var = 10; //Integer |
Join online php and python class at sstech lab noida.
The necessary steps to create a MySQL database using PHP are:
PHP parser parses the PHP developed website from the opening to the closing tag. Tags indicate that from where PHP code is being started and ended. In other words, opening and closing tags decide the scope of PHP scripting syntax of closing tag in PHP
<?php syntax of opening tag in PHP
?> syntax of closing tag in PHP
A cookie is used to identify a user. A cookie is a little record that the server installs on the client's Computer. Each time a similar PC asks for a page with a program, it will send the cookie as well. With PHP, you can both make and recover cookie value.
Some important points regarding Cookies:
The Include() function is used to put data of one PHP file into another PHP file. If errors occur, then the include() function produces a warning but does not stop the execution of the script, and it will continue to execute.
The Require() function is also used to put data of one PHP file to another PHP file. If there are any errors, then the require() function produces a warning and a fatal error and stops the script.
A persistent cookie is permanently stored in a cookie file on the browser's computer. By default, cookies are temporary and are erased if we close the browser.
The PHP split() function splits string into an array by regular expression.
The PHP explode() function breaks a string into an array.
The .htaccess is a configuration file on Apache server. You can change configuration settings using directives in Apache configuration files like .htaccess and httpd.conf.
CRYPT() and MD5()
The exit() function is used to stop the execution of PHP script.
There are 3 types of error in PHP.
By default, the maximum execution time for PHP scripts is set to 30 seconds. If a script takes more than 30 seconds, PHP stops the script and returns an error.
You can change the script run time by changing the max_execution_time directive in the php.ini file.
When a script is called, set_time_limit function restarts the timeout counter from zero. It means, if default timer is set to 30 sec, and 20 sec is specified in function set_time_limit(), then script will run for 45 seconds. If 0sec is specified in this function, script takes unlimited time.
Since PHP 4.3, mysql_reate_db() is deprecated. Now you can use the following 2 alternatives.
The mysqli_connect() function is used to create a connection in PHP.
There are two methods to connect MySQL database with PHP. Procedural and object-oriented style.
The mail() function is used to send email in PHP.
The readfile() function is used to download the file in PHP.
The move_uploaded_file() function is used to upload file in PHP.
You should just run the PHP command line interface (CLI) and specify the file name of the script to be executed as follows.
The unlink() function is used to delete a file in PHP.
PHP fwrite() and fputs() functions are used to write data into file. To write data into a file, you need to use w, r+, w+, x, x+, c or c+ mode.
PHP provides various functions to read data from the file. Different functions allow you to read all file data, read data line by line, and read data character by character.
PHP file read functions are given below:
PHP fopen() function is used to open file or URL and returns resource. It accepts two arguments: $filename and $mode.
Syntax:
The main difference between session and cookie is that cookies are stored on user's computer in the text file format while sessions are stored on the server side.
Cookies can't hold multiple variables, on the other hand, Session can hold multiple variables.
You can manually set an expiry for a cookie, while session only remains active as long as browser is open.
PHP session_start() function is used to start the session. It starts new or resumes the current session. It returns the current session if the session is created already. If the session is not available, it creates and returns new sessions.
PHP Engine creates a logical object to preserve data across subsequent HTTP requests, which is known as session.
Sessions generally store temporary data to allow multiple PHP pages to offer a complete functional transaction for the same user.
Simply, it maintains data of an user (browser).
PHP setcookie() function is used to set cookie with HTTP response. Once the cookie is set, you can access it by $_COOKIE superglobal variable.
Syntax:
Require and include both are used to include a file, but if data is not found include sends warning whereas require sends Fatal error.
PHP allows you to include file so that page content can be reused again. There are two ways to add the file in PHP.
You can use JavaScript submit() function to submit the form without explicitly clicking any submit button.
There are two methods GET and POST.
There are many array functions in PHP:
The strlen() function is used to get the length of the string.
The indexed array holds elements in an indexed form which is represented by number starting from 0 and incremented by 1. For example:
The associative array holds elements with name. For example:
There are many array functions in PHP:
There are three types of array in PHP:
An array is used to store multiple values in a single value. In PHP, it orders maps of pairs of keys and values. It saves the collection of the data type.
The isset() function checks if the variable is defined and not null.
The header() function is used to send a raw HTTP header to a client. It must be called before sending the actual output. For example, you can't print any HTML element before using this function.
The PHP count() function is used to count total elements in the array, or something an object.
PHP magic constants are predefined constants, which change based on their use. They start with a double underscore (__) and end with a double underscore (__).
A PHP variable is the name of the memory location that holds data. It is temporary storage.
Syntax:
PHP has borrowed its syntax from Perl and C.
The scope of a variable is the context within which it is defined. For the most part, all PHP variables only have a single scope. This single scope spans included and required files as well.
$_COOKIE is an associative array of variables sent to the current PHP script using the HTTP Cookies
$_ENV is an associative array of variables sent to the current PHP script via the environment method.
$_FILES is an associative array composed of items sent to the current script via the HTTP POST method.
$_SERVER is an array including information created by the web server such as paths, headers, and script locations.
The session_unregister() function unregister a global variable from the current session and the session_unset() function frees all session variables.
Sessions automatically end when the PHP script finishes executing but can be manually ended using the session_write_close().
You can propagate a session id via cookies or URL parameters.
The use of the function session_start() lets us activating a session.
A session is a logical object enabling us to preserve temporary data across multiple PHP pages.
No, a parent constructor have to be called explicitly as follows:
parent::constructor($value)
In PHP, objects passed by value.
The unset() function is dedicated for variable management. It will make a variable undefined.
The result set can be handled using mysqli_fetch_array, mysqli_fetch_assoc, mysqli_fetch_object or mysqli_fetch_row.
If we would like to pass values through a form or an URL, then we need to encode and to decode them using htmlspecialchars() and urlencode().
We use the operator '==' to test is two objects are instanced from the same class and have same attributes and equal values. We can test if two objects are referring to the same instance of the same class by the use of the identity operator '==='.
'final' is introduced in PHP5. Final class means that this class cannot be extended and a final method cannot be overridden.
PHP supports only single inheritance; it means that a class can be extended from only one single class using the keyword 'extended'.
The $var (single dollar) is a normal variable with the name var that stores any value like string, integer, float, etc.
The $$var (double dollar) is a reference variable that stores the value of the $variable inside it.
A PHP variable is the name of the memory location that holds data. It is temporary storage.
Syntax:
Echo can output one or more string but print can only output one string and always returns 1.
Echo is faster than print because it does not return any value.
PHP print output a string. It is a language construct not a function. So the use of parentheses is not required with the argument list. Unlike echo, it always returns 1.
Syntax:
PHP echo output one or more string. It is a language construct not a function. So the use of parentheses is not required. But if you want to pass more than one parameter to echo, the use of parentheses is required.
Syntax:
PHP4 doesn't support oops concept and uses Zend Engine 1.
PHP5 supports oops concept and uses Zend Engine 2.
The scripting engine that powers PHP is called Zend Engine 2.
In static websites, content can't be changed after running the script. You can't change anything on the site. It is predefined.
In dynamic websites, content of script can be changed at the run time. Its content is regenerated every time a user visit or reload. Google, yahoo and every search engine is the example of dynamic website.
$GLOBALS is associative array including references to all variables which are currently defined in the global scope of the script.
The session_unregister() function unregister a global variable from the current session and the session_unset() function frees all session variables.
Sessions automatically end when the PHP script finishes executing but can be manually ended using the session_write_close().
You can propagate a session id via cookies or URL parameters.
The use of the function session_start() lets us activating a session.
A session is a logical object enabling us to preserve temporary data across multiple PHP pages.
We have to enable the Magic quotes entry in the configuration file of PHP.
The stripslashes function enables us to remove the escape characters before apostrophes in a string.
The unset() function is dedicated for variable management. It will make a variable undefined.
The unlink() function is dedicated for file system handling. It simply deletes the file given as entry.
The mysqli_fetch_object() function collects the first single matching record where mysqli_fetch_array() collects all matching records from the table in an array.
To be able to display a human-readable result we use print_r().
require(), and require_once() perform the same task except that the second function checks if the PHP script is already included or not before executing it.
If we would like to pass values through a form or an URL, then we need to encode and to decode them using htmlspecialchars() and urlencode().
It is possible to generate HTML through PHP scripts, and it is possible to pass pieces of information from HTML to PHP.
'final' is introduced in PHP5. Final class means that this class cannot be extended and a final method cannot be overridden.
PHP supports only single inheritance; it means that a class can be extended from only one single class using the keyword 'extends'.
PHP 5 presents many additional OOP (Object Oriented Programming) features.
To be able to display the output directly to the browser, we have to use the special tags <?= and ?>.
The two most common ways to start and finish a PHP script are:
<?php [ --- PHP code---- ] ?> and <? [--- PHP code ---] ?>
Just use the PHP command line interface (CLI) and specify the file name of the script to be executed as follows:
php script.php
PHP means-> PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor.
At begining PHP known as "Personal Home Page"
Current Version 7.4 of PHP.
PEAR means "PHP Extension and Application Repository". It extends PHP and provides a higher level of programming for web developers.
PHP syntax resembles Perl and C.
'final' is introduced in PHP5. Final class means that this class cannot be extended and a final method cannot be overridden.
In static websites, content can't be changed after running the script. You can't change anything on the site. It is predefined.
In dynamic websites, content of script can be changed at the run time. Its content is regenerated every time a user visit or reload. Google, yahoo and every search engine is the example of dynamic website.
It is an open source server-side scripting language which is widely used for web development. It supports many databases like MySQL, Oracle, Sybase, Solid, PostgreSQL, generic ODBC etc. PHP stands for PHP: Hypertext Pre-processor, that earlier stood for Personal Home Pages. Rasmus Lerdorf known as the father of PHP.